Loops

While, Foreach, or For Loop…which one do I want to use?
Prerequisite
This page assumes you have completed the Coding Intro lesson.
Intro
Loops are handy tools in programming because they allow repetitive tasks to run over and over until a condition is met. That condition can be a count, to loop/run for a specific number of times. Here we will demonstrate three kinds of loops and which one to use to get your code to do what you want it to do.
While Loop
The while loop is a conditional loop. This type of loop runs until a specific condition is met.
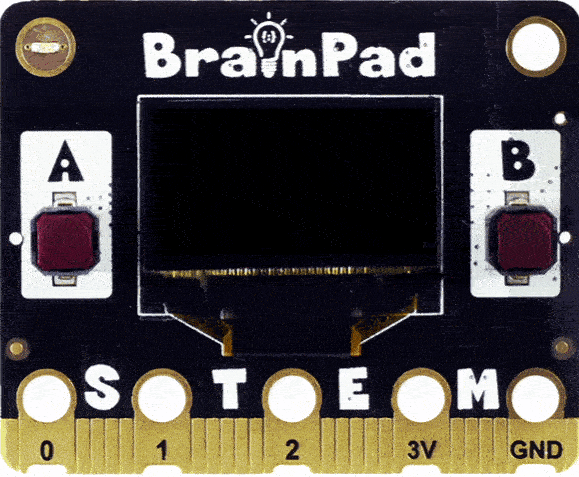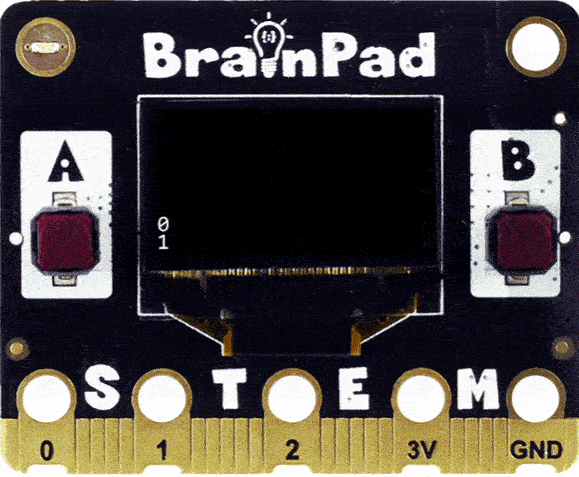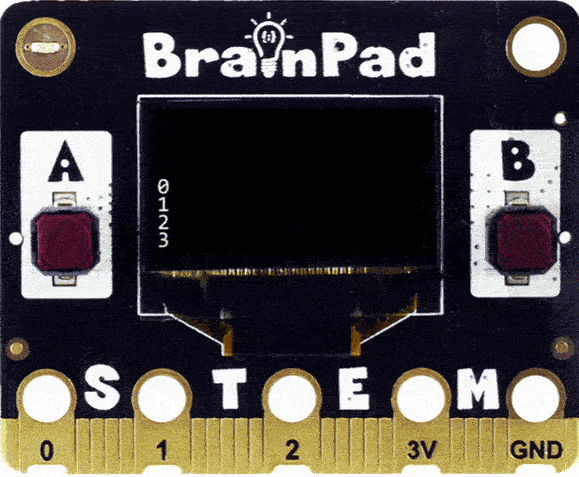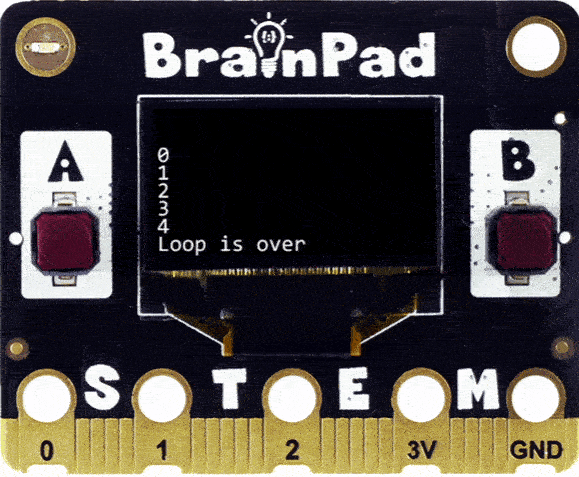
let x=0;
while(x<5){
await BrainPad.System.Println(x);
x=x+1;
}
await BrainPad.System.Println("Loop is over");
In this code example, the while loop only runs while x <5. Once x reaches 5, the loop is terminated.
The while loop is also handy for creating loops that NEVER END and continue running forever. We create this type of loop by just adding the word True to the condition. Since the condition is always true, it keeps running.
This next example is a code for a seconds counter. We are using Wait(1) to force the program to pause (wait) for one second.
let count = 0;
while(true) {
await BrainPad.System.Println(count);
count = count + 1;
await BrainPad.System.Wait(1000);
}
//This line of code is never reached.
await BrainPad.System.Println("You will never see this!");
For Loop
A for loop counts through a range. The syntax for the for-loop in JavaScript is similar to C/C#.
for (let i=0 ; i<5 ; i=i+1){
await BrainPad.System.Println(i);
}
await BrainPad.System.Println('Loop is over'); 
The for loop has three sections. First is the initialize section that runs when the loop starts, which is let i=0 in the example above. The second section is what condition to check for in each loop (similar to the while-loop), and that is i<5. Finally, the last section is what change will happen to the variable in each loop. In this case it is i=i+1, which will increment the variable by one.
Foreach Loop
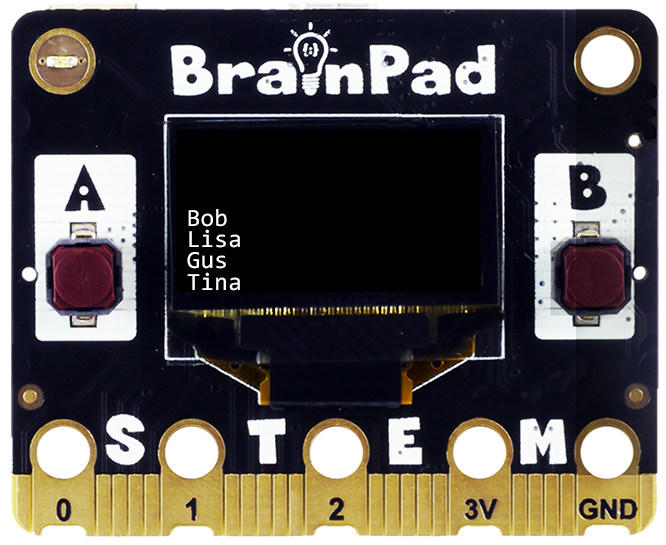
We can use a foreach loop to loop through a list of values, like an array of names. However, forEach in JavaScript can’t run asynchronously. This will cause problems when accessing hardware. A better approach is to use For-of loop.
let nameList = ["Bob","Lisa","Gus","Tina"];
for(const name of nameList) {
await BrainPad.System.Println(name);
}
What’s Next?
Loops are great, but to get the full power of coding we need to check and run code based on a specific condition to handle the program’s Flow Control.
BrainStorm
Loops help computers in repeating tasks. To print 1 to 3, we can just input three lines, but how do we count to 100? Can you make a loop that prints all even numbers up to 100?
let x=0;
while(x<100){
await BrainPad.System.Println(x);
x=x+2;
}